Optimizing Data Interpretation: Google Analytics Secondary Dimension Explained
Optimizing Data Interpretation: Google Analytics Secondary Dimension Explained
Blog Article
Unlocking the Power of Second Dimension Analytics for Boosted Data Insights and Decision-Making
In the world of data analytics, key measurements usually take the limelight, yet the real deepness of insights lies within the realm of second measurements. By using the power of second measurement analytics, organizations can unveil covert trends, reveal relationships, and remove a lot more significant conclusions from their data.
Relevance of Second Dimensions
Exploring the significance of second measurements in analytics reveals the hidden layers of information understandings important for informed decision-making in various domain names. Additional dimensions give a much deeper understanding of primary information by using additional context and viewpoints. By integrating secondary measurements into analytics, organizations can remove much more thorough and nuanced insights from their datasets.
One key value of secondary measurements is their capability to sector and categorize main information, enabling for a more in-depth analysis of details subsets within a dataset. This division enables organizations to determine patterns, fads, and outliers that may not be noticeable when checking out the information all at once. Furthermore, second measurements help in uncovering relationships and dependences between various variables, bring about even more precise projecting and anticipating modeling.
Additionally, second measurements play an essential function in boosting information visualization and reporting. By adding additional measurements to visualizations, such as charts or charts, analysts can create much more insightful and informative representations of data, assisting in far better interaction of searchings for to stakeholders. Overall, the integration of secondary dimensions in analytics contributes in unlocking the full capacity of data and driving evidence-based decision-making.
Secret Benefits of Using Additional Dimensions
Making use of additional dimensions in analytics supplies companies a tactical benefit by increasing the depth and granularity of information insights. By studying data using second dimensions such as time, area, gadget kind, or individual demographics, organizations can discover patterns, trends, and relationships that may or else stay surprise.
Moreover, the application of secondary measurements enhances the context in which main information is analyzed. By leveraging second dimensions in analytics, organizations can harness the full capacity of their information to drive far better decision-making and achieve their company goals.
Advanced Information Evaluation Strategies
A deep study advanced data analysis techniques exposes advanced techniques for removing beneficial understandings from intricate datasets. One such strategy is machine learning, where algorithms are employed to identify patterns within data, predict outcomes, and make data-driven decisions. This method allows for the automation of logical version structure, making it possible for the handling of huge quantities of data at a quicker pace than conventional methods.
Another advanced strategy is anticipating analytics, which makes use of analytical algorithms and device learning techniques to anticipate future end results based on historical information. By assessing patterns and patterns, companies can anticipate consumer actions, market patterns, and potential risks, encouraging them to make positive see this decisions.
Furthermore, message mining and belief evaluation are useful techniques for removing understandings from unstructured information resources such as social media remarks, client reviews, and study actions. By evaluating message data, organizations can comprehend consumer point of views, identify arising patterns, and enhance their solutions or products based upon feedback.
Enhancing Decision-Making Via Secondary Measurements
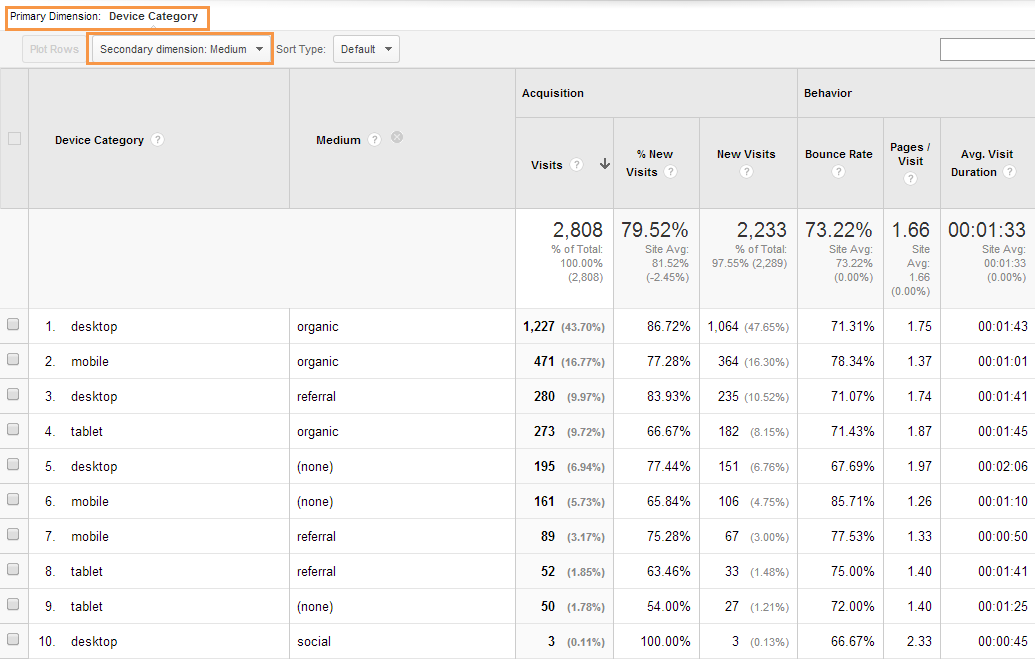
Enhancing decision-making via secondary measurements enables companies to make even more informed and targeted calculated selections. For example, by segmenting client information based upon secondary measurements like acquiring history or interaction degrees, firms can tailor their advertising methods to specific audience sections, bring about boosted conversion rates and customer satisfaction. Second measurements can aid recognize relationships and partnerships in between different variables, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions that drive growth and profitability.
Implementing Second Measurement Analytics
When including additional dimensions in analytics, organizations can unlock much deeper understandings that drive calculated decision-making and improve overall performance. Applying second measurement analytics needs a structured strategy to make certain efficient use of this powerful device. The initial step is to identify the vital metrics and measurements that line up with the organization's critical goals. This entails recognizing the certain questions the company looks for to answer and the information points required to resolve them.
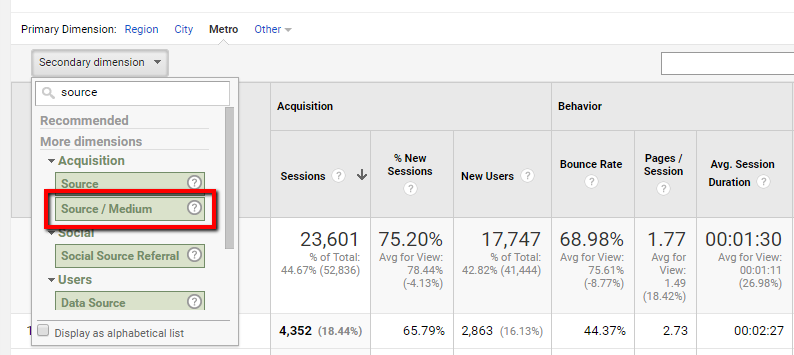
Moreover, companies ought to utilize advanced analytics devices and modern technologies to improve the procedure of useful reference incorporating additional measurements. These tools can automate information handling, analysis, and visualization, enabling companies to focus on translating understandings rather than hands-on information adjustment.
Conclusion
In final thought, additional measurement analytics play a vital duty in boosting information understandings and decision-making procedures. By using sophisticated information analysis methods and executing additional dimensions efficiently, organizations can unlock the power of their information to drive critical organization choices.
In the world of information analytics, main dimensions frequently take the spotlight, yet the real deepness of insights lies within the realm of second measurements.Using secondary dimensions in analytics supplies companies a calculated advantage by augmenting the deepness and granularity of data insights. By leveraging additional dimensions in analytics, companies can harness the full capacity of their information to drive better decision-making and achieve their service objectives.
Carrying out information validation processes and routine audits can aid maintain information quality and reliability.
By making use of innovative data analysis strategies and applying second measurements effectively, companies can unlock the power of their data to drive critical business decisions.
Report this page